Authors: Logan Lebanoff, Kaiqiang Song, Franck Dernoncourt, Doo Soon Kim, Seokhwan Kim, Walter Chang, Fei Liu
Paper reference: https://aclanthology.org/P19-1209.pdf
Contribution
This paper falls into the line of extract-then-abstract line of summary generation. It focuses on selecting summary-worthy sentence singletons and pairs and uses them as the basis for summary generation. This is based on an observation that 60-85% of summary sentences are generated by fusing one or two source sentences from three datasets (CNN/DM, XSum, DUC-04) experimented with.
More specifically, it first creates all possible sentence singletons and pairs (call them instances) and then uses a BERT model to determine whether an instance is appropriate to be selected in the first place. These selected instances are then treated as the input for later abstractive summarization. At the inference time, the summarization receives an instance from BERT and outputs a summary sentence, then repeats this process to generate several sentences. There should be some coherence problems since these summary sentences are generated separately.
Details
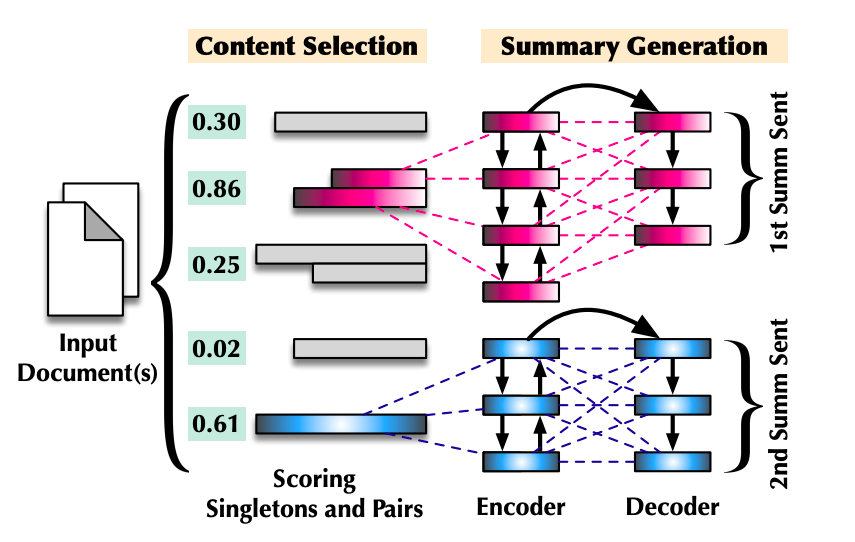
Model structure illustration: a sentence pair is chosen (red) and then merged to generate the first summary sentence. Next, a sentence singleton is selected (blue) and compressed for the second summary sentence.